DFA® Tools
The DFA tool is used in the first part of the process for preventive optimization of product costs and improvement of quality.
Deployment
The DFA tool is used in the first part of the process for preventive optimization of product costs and improvement of quality.
The first application takes place during the concept phase of new products or at the start of ratio projects.
Essentially, it is used to optimize the complexity of a product.
Simplifying assembly, processes (including logistics), and supporting and accelerating teamwork among project teams.
Procedure
Interactive questions posed to a team of specialists lead to new and better solutions. The same approach, interactive questioning, is also used to examine the manufacturability of this new solution in terms of cost and quality optimization. The characteristic values and cost values determined in parallel by the DFA tool help to further optimize the solutions in a cost-oriented manner in the next step of detailing.
The service thus supports the team in the gradual optimization process from rough to fine, i.e., in finding the first conceptual solutions, working out the details, and obtaining the various approvals from the detailing stage through prototypes to the start of production.
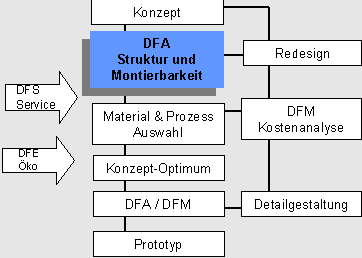
The DFA-Tool
Asks questions regarding functionality (physical level) and cost-influencing aspects such as: structure (product complexity), runtimes, and mountability.
The values determined by the tool regarding the expected effort (assembly times, assembly costs) and characteristic values indicate how easy or difficult the product to be manufactured will be.
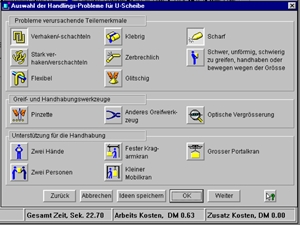
An example from the various “DFA question windows”
Specifically illustrated here are handling, joining, and transport problems, as well as questions regarding the analysis of functional demarcation.
The display shows, for example, the assembly time and costs for the expenses recorded to date, any problems encountered with the part under investigation, and the costs for the entire product.
The DFA question windows
Are designed to perform DFA analysis when answering questions.
Based on part geometry, handling and joining problems, and a minimum of part criteria.
This variable information enables the responsible engineers/designers to make decisions, e.g., where and in which direction optimization should be carried out based on specific costs and times, with the aim of making the product as cost-effective as possible or increasing safety.
During the learning process and exchange of information, the complete procedures and operations are displayed directly on the structure list. The results appear as a block in the tree structure.
These questions all relate to the appearance of the product design, how they affect the overall assembly time and costs, and can then be seen on the structure list.
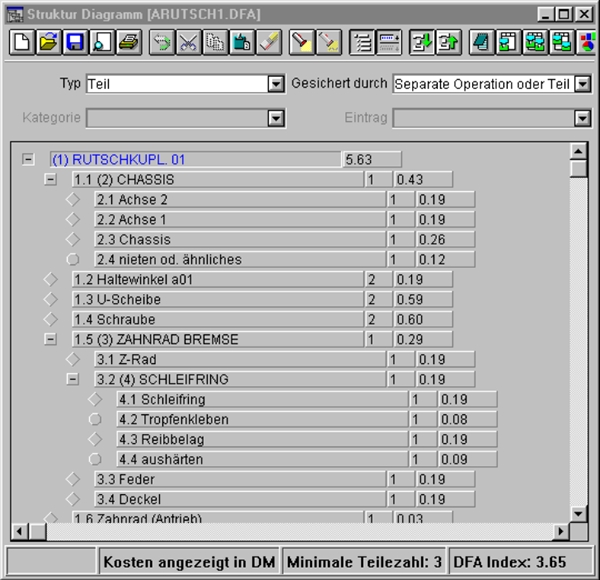
Example of a DFA window
The costs for a specific selected quantity are visible at a glance.
The following information is also displayed in additional SW masks/graphics:
- Complexity
- Installation times & costs
- Costs for parts and their tools
- Suggestions for improvement
- Characteristic value for simplicity
- Difficulty of the solution
- Comparison of solutions and their costs
- Savings from different solutions
- Total values, e.g., product costs, tool costs
Proposals for redesign
The graphics and suggestions for redesign options not only allow for quick review and presentation of the analysis results, they also enable comparison of the results of multiple analyses (variants or what-if analyses).
Get started now!
In the DFMA forum, you will learn about the DFMA methodology using a case study and numerous application examples.
